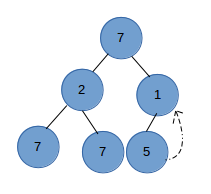
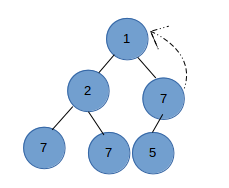
什么是Heap1 ?
数据结构中的Heap是一种满足heap property的树:
- 父节点和子节点按照给定顺序, 并应用在整棵树上
根据父节点和子节点不同顺序又可以分为:
-
min-heap(最小堆):
- 父节点比子节点小
- 最小值在根节点
-
max-heap(最大堆):
- 父节点比子节点大
- 最大值在根节点
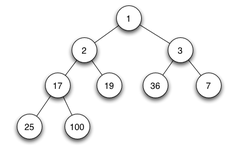
比较常用的堆是二叉堆,在结构上是一个complete binary tree。 因此,对于N个节点的二叉堆,高度是 logN 。 二叉堆不同于二叉查找树, 即按照in-order遍历不会使数据有序,二叉堆每个节点和它的silblings并没有什么关系。
数据结构中的Heap不要和memory中的heap混淆。
更详细的信息可以参考wikipedia
为什么要用到Heap1?
通过上面对Heap的了解,我们可以知道下面几种情况可能比较适合使用Heap:
- 需要sort或partially sort的应用
- 需要取极值的情况
- 需要优先级的场景
常用的priority queue其实就是用Heap来实现的。
怎么实现?
由于heap是complete binary tree, 如果使用数组来实现,那么我们知道一个node的index, 怎么知道左右child呢? 根据complete binary tree我们可以得到:
left = 2 * index , right = 2 * index + 1
Heap上常用的操作
- find-min/find-max : 取得极值
根据heap property可知, 只需要返回root节点即可
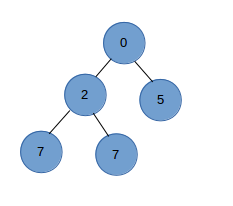
- extract-min/extract-max : 删除极值
要删除root节点, 首先我们可以用最后一个节点覆盖root节点, 然后比较新的root节点和左右子节点来rebalance 二叉堆
假设我们二叉堆是这样的
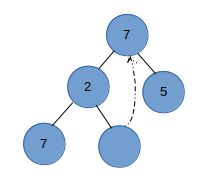
首先我们用the last node覆盖root节点
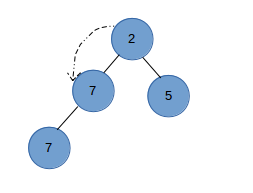
然后比较新的root节点和左右节点,交换父节点和左子节点来保持heap property
如果交换后左子树违反heap property,则重复上面步骤,只到整个二叉堆满足heap property
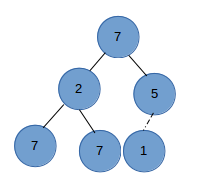
- insert :插入一个值, 可能violate heap property, 需要rebalance 二叉堆
要插入一个值,我们可以先作为最后一个节点,然后与父节点比较
假设我们二叉堆是这样的
首先将新值作为最后一个节点
与父节点比较发现违反heap property,则与父节点交换
重复上面步骤知道满足heap property
- empty/size : 需要得到heap大小或判断是否为空
- replace : 替换一个值, 需要重新rebalance
代码
根据上面分析, 我们可以很方便的写出二叉堆的实现, 下面是我用C++的实现代码。
二叉堆的类声明如下:
template<typename T, typename comparator = std::less<T> >
class heap {
public:
// empty arguments constructor
heap(comparator cmp = comparator());
// one argument constructor ( default comparator )
heap(const std::vector<T> &nums, comparator cmp = comparator());
// iterator constructor
// copy constructor
heap(const heap *other);
// assign constructor
const heap &operator=(const heap *other);
// find min/max
const T top() const;
// extract top
void pop();
// insert value
void push(T val);
// size -- returns the number of elements
const size_t size() const;
// empty -- checks whether the heap is empty
const bool empty() const;
// destructor
~heap();
private:
std::vector<T> data;
comparator comp;
void percolateDown(int idx);
void percolateUp(int idx);
};
上面的二叉堆类的一个默认参数的构造函数:
// one default argument constrctor
template<typename T, typename comparator>
heap<T,comparator>::heap(comparator cmp) : comp(cmp) {
// just initialize the data to size 1
data.resize(1);
//this->comp = cmp;
}
二叉堆的两个参数构造函数(第二个参数有默认值):
// two argument constructor
template<typename T, typename comparator>
heap<T, comparator>::heap(const std::vector<T> &nums, comparator cmp) {
this->data.resize(nums.size()+1);
this->comp = cmp;
// copy nums to data
copy(nums.begin(), nums.end(), data.begin()+1);
// balance the heap
for(int idx = this->size()/2;idx > 0;--idx)
percolateDown(idx);
}
复制构造函数, 需要deep copy数据:
// copy constructor
template<typename T, typename comparator>
heap<T,comparator>::heap(const heap *other) {
copy(other->data.begin(), other->data.end(), this->data.begin());
this->comp = other->comp;
}
赋值构造函数,和复制构造函数类似, 需要deep copy,另外需要返回本身引用:
// assign constructor
template<typename T, typename comparator>
const heap<T,comparator>& heap<T,comparator>::operator =(const heap *other) {
copy(other->data.begin(), other->data.end(), this->data.begin());
this->comp = other->comp;
return this;
}
Destructor函数:
// destructor
template<typename T, typename comparator>
heap<T,comparator>::~heap() {
}
top()函数实现,只需要在数据非空情况下返回第一个数据即可:
// find-min/max
template<typename T, typename comparator>
const T heap<T,comparator>::top() const {
if( !empty() )
return data[1];
}
pop()函数,由于要删掉极值, 要重新rebalance二叉堆。我们用最后一个值覆盖极值,并重新build二叉堆:
// remove the top element
template<typename T, typename comparator>
void heap<T,comparator>::pop() {
if( !empty() ) {
data[1] = data[size()];
data.resize(size());
percolateDown(1);
}
}
push()函数,我们把要插入值加入到数据后面,并根据二叉堆property来重新balance二叉堆:
// insert an element
template<typename T, typename comparator>
void heap<T,comparator>::push(T val) {
this->data.push_back(val);
percolateUp(size());
}
empty()函数,指示二叉堆是否为空:
// check whether the heap is empty
template<typename T, typename comparator>
const bool heap<T,comparator>::empty() const {
return this->size() == 0;
}
size()函数, 返回二叉堆的大小:
// get the size of the heap
template<typename T, typename comparator>
const size_t heap<T,comparator>::size() const {
return this->data.size() - 1;
}
percolateDown(int idx)函数,根据二叉堆属性把数据往下移来rebalance二叉堆:
// private functions
// affter extracting root value, rebalance the heap
template<typename T, typename comparator>
void heap<T,comparator>::percolateDown(int idx) {
if( idx > this->size()/2 )
return;
int midx = idx;
if( comp(data[2*idx],data[midx]) )
midx = 2 * idx;
if( 2 * idx + 1 <= this->size() && comp(data[2*idx+1],data[midx]) )
midx = 2 * idx + 1;
if( midx != idx ) {
std::swap(data[midx], data[idx]);
percolateDown(midx);
}
}
percolateUp(int idx)与上面函数相反,把数据往上移来rebalance二叉堆:
// after insert new element into heap, we need percolateup the element to
// rebalance the heap
template<typename T, typename comparator>
void heap<T,comparator>::percolateUp(int idx) {
if( idx <= 1 )
return;
if( comp(data[idx] , data[idx/2]) ) {
std::swap(data[idx], data[idx/2]);
percolateUp(idx/2);
}
}
以上是priority queue使用heap结构完整实现, 接下来我用实现的二叉堆做了常用的堆排序 代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include "Heap.hpp"
#include<cstddef>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<random>
using namespace std;
void gen_array(int n, vector<int> & data, int base_start = 1, int base_end = 99) {
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
data.push_back( rand() % (base_end - base_start) + base_start );
}
void print_array(vector<int> & data, const string s) {
cout << s << " : ";
for(int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++)
cout << data[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void heapSort(vector<int> &nums) {
heap<int> pq(nums);
nums.resize(0);
while(!pq.empty() ) {
nums.push_back(pq.top());
pq.pop();
}
}
int main() {
cout << "test one argument constructor and top() && pop() member function\n";
vector<int> nums;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int n = rand() % 27;
gen_array(n, nums);
print_array(nums,"Data");
heapSort(nums);
print_array(nums,"Sort");
// C++ random number generator
// common use case: binding a RNG with a distribution
default_random_engine e;
uniform_int_distribution<> d(0, 10);
function<int()> rnd = std::bind(d, e); // a copy of e is stored in rnd
cout << "test push() member function\n";
nums.push_back(rnd());
heap<int> pq(nums);
pq.push(rnd());
nums.resize(0);
while(!pq.empty() ) {
nums.push_back(pq.top());
pq.pop();
}
print_array(nums,"Sort");
cout << "test max-heap\n";
nums.push_back(rnd());
heapSort_reverse(nums);
print_array(nums,"Sort");
cout << "test default no-argument constructor\n";
heap<int> emptyPQ;
int k = rnd();
cout << "Data = ";
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
int val = rnd();
cout << val << "\t";
emptyPQ.push(val);
}
cout << endl << "Sort = ";
while(!emptyPQ.empty() ) {
cout << emptyPQ.top() << "\t";
emptyPQ.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
上面测试程序输出:
test one argument constructor and top() && pop() member function
Data : 37 60 29 43 52 81 15 35
Sort : 15 29 35 37 43 52 60 81
test push() member function
Sort : 0 1 15 29 35 37 43 52 60 81
test max-heap
Sort : 0 1 8 15 29 35 37 43 52 60 81
test default no-argument constructor
Data = 5 2 0 7 7
Sort = 0 2 5 7 7