Red-Black Tree
什么是Red-Black Tree ?
上面说过, 在最坏情况下,BST会退化成link-list,其时间复杂度是O(n)。因此为了保证O(logn)的时间复杂度,需要设计一种能够使Tree保持平衡的机制。这儿的Red-Black Tree就是一种自平衡的二叉查找树。
Red-Black Tree是符合下面定义的二叉树:
- 任意节点值比其左子树所有节点值大,比右子树所有节点小。(BST的定义)
- 任意节点要么是黑色要么是红色
- 根节点必须是黑色
- 所有的叶子节点(nil)都是黑色
- 如果一个节点是红色,则其左右子节点必须是黑色
- 从任意节点到叶子节点(nil)所有path上的黑色节点个数相同

上面说满足这些约束的就是Red-Black Tree,是能够保证O(logn)最坏时间复杂度的自平衡的二叉查找树。真的是这样吗?假设从一个节点到叶子节点的path上黑色节点个数(不算叶子节点)为B,则最长path上能够有的最多的节点个数为2*B(黑红节点交叉), 而最短的path上的节点最少也要有B个(全是黑色节点)。因此对于一个Red-Black Tree, 没有path会比其他path长两倍。这就保证了Red-Black Tree的高度大致保持平衡,而Red-Black Tree上各种操作和高度是
Red-Black Tree的实现
既然Red-Black Tree也是二叉查找树, 自然能够在BST上实现的操作必然能够在Red-Black Tree上实现:
- 插入, 有插入数据我们才能进行其他操作
- 删除, 删除不需要的值
- 查找, 由于BST的性质, 我们知道在BST上可以实现二分查找
- 遍历, 对于BST来讲,就是
in-order-traversal了
查找和遍历由于没有写操作,和BST上相关操作一致即可。而插入和删除由于改变了树可能会违反Red-Black Tree约束,需要一些额外操作来使树重新满足约束。
代码
- 首先, 我们声明一个RBT类,
包含上面所描述的四种操作。我们使用
TreeNode作为RBT的节点,和上面的BST<T>类似。
// Binary search Tree declaration
template<typename T>
class RBT {
public:
// default constructor
explicit RBT();
// copy constructor
RBT(const RBT &other);
// assignment constructor
const RBT<T>& operator=(const RBT &other);
// destructor
~RBT();
enum Color { RED, BLACK };
// TreeNode definition
class TreeNode {
public:
friend class RBT;
T val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode *parent;
// indicate this node's color
Color color;
// constructor
TreeNode() : left(nullptr), right(nullptr), parent(nullptr), color(BLACK){};
TreeNode(T v) : val(v), left(nullptr), right(nullptr), parent(nullptr), color(RED){};
TreeNode(T v, TreeNode *l, TreeNode *r, TreeNode *p = nullptr, Color c = RED) : val(v), left(l), right(r),parent(p), color(c){};
};
// STL-style iterator
class iterator {
public:
friend class RBT;
explicit iterator();
const iterator& operator=(const iterator &other); // assignment constructor
iterator& operator++(); // prefix increment
iterator operator++(int); // postfix increment
T& operator*() const; // derefence the pointer
bool operator!=(const RBT<T>::iterator &other) const;
bool operator==(const RBT<T>::iterator &other) const;
// for iterator_traits to refer
typedef std::output_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef std::ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef T* pointer;
typedef T& reference;
private:
iterator(TreeNode* n);
TreeNode* node;
TreeNode* lastNode;
};
// iterator begin() and end()
iterator begin() const;
iterator end() const;
// insert an element into RBT
void insert(T v);
// find an element
iterator find(const T& v) const;
//const_iterator find(const T& v) const;
// remove one element
void erase(iterator itr);
// return the size of RBT
const std::size_t size() const;
// check whether the RBT is nullptr
const bool empty() const;
private:
int cnt;
TreeNode *root;
// private insert helper function
void insert(T v, TreeNode *&r, TreeNode * const &p = nullptr);
void insert_case1(TreeNode *r);
void insert_case2(TreeNode *r);
void insert_case3(TreeNode *r);
void insert_case4(TreeNode *r);
void insert_case5(TreeNode *r);
TreeNode* grandParent(TreeNode * const &r) const;
TreeNode* uncle( TreeNode * const &r) const;
TreeNode* sibling( TreeNode * const &r) const;
// private : replace node in parent
void replace_node_in_parent(TreeNode *node, TreeNode *newNode = nullptr);
// delete helper functions
void delete_case1(TreeNode *node);
void delete_case2(TreeNode *node);
void delete_case3(TreeNode *node);
void delete_case4(TreeNode *node);
void delete_case5(TreeNode *node);
void delete_case6(TreeNode *node);
// rotate the node
void rotate_right(TreeNode *r);
void rotate_left(TreeNode *r);
// private : find the max value node
TreeNode *findMax(TreeNode *node);
};
RBT<T>::iterator实现, 这一部分与BST一样
// RBT<T>::iterator
// default constructor
template<typename T>
RBT<T>::iterator::iterator() {
node = nullptr;
lastNode = nullptr;
}
// one argument constructor
template<typename T>
RBT<T>::iterator::iterator(TreeNode* n) {
node = n;
lastNode = nullptr;
}
// assignment constructor
template<typename T>
const typename RBT<T>::iterator& RBT<T>::iterator::operator=(const iterator &other) {
this->node = other.node;
return *this;
}
template<typename T>
T& RBT<T>::iterator::operator*() const {
return this->node->val;
}
// overload operator ==
template<typename T>
bool RBT<T>::iterator::operator==(const RBT<T>::iterator &other) const {
return this->node == other.node;
}
// overload operator !=
template<typename T>
bool RBT<T>::iterator::operator!=(const RBT<T>::iterator &other ) const {
return this->node != other.node;
}
// overload prefix ++
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::iterator& RBT<T>::iterator::operator++() {
// if current node is root , we could get the lastNode
if( node->parent == nullptr ) {
lastNode = node;
while( lastNode->right )
lastNode = lastNode->right;
}
if( node->right != nullptr ) {
node = node->right;
while( node->left )
node = node->left;
} else if( node == lastNode ){
node = nullptr;
} else if( node == node->parent->left ) {
node = node->parent;
} else if( node == node->parent->right ) {
while( node->parent->val <= node->val )
node = node->parent;
node = node->parent;
}
return *this;
}
// overload postfix ++
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::iterator RBT<T>::iterator::operator++(int) {
// if current node is root , we could get the lastNode
if( node->parent == nullptr ) {
lastNode = node;
while( lastNode->right )
lastNode = lastNode->right;
}
TreeNode *p = this->node;
if( node->right != nullptr ) {
node = node->right;
while( node->left )
node = node->left;
} else if( node == lastNode ){
node = nullptr;
} else if( node == node->parent->left ) {
node = node->parent;
} else if( node == node->parent->right ) {
while( node->parent->val <= node->val )
node = node->parent;
node = node->parent;
}
return iterator(p);
}
RBT<T>无参数构造函数
// default constructor -- only initialize the private variable
template<typename T>
RBT<T>::RBT() {
cnt = 0;
root = nullptr;
}
RBT<T>复制构造函数,需要实现deep copy
// copy constructor -- deep copy every element of the other RBT
template<typename T>
RBT<T>::RBT(const RBT &other) {
cnt = other.cnt;
if( cnt == 0 )
return;
std::queue<std::pair<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> > q;
q.push(std::make_pair(root(other.root->val),other.root));
while( !q.empty() ) {
TreeNode *node1 = q.front().first;
TreeNode *node2 = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if( node2->left ) {
node1->left = new TreeNode(node2->left->val);
node1->left->parent = node1;
q.push(make_pair(node1->left, node2->left));
}
if( node2->right ) {
node1->right = new TreeNode(node2->right->val);
node1->irght->parent = node1;
q.push(make_pair(node1->right, node2->right));
}
}
}
RBT<T>赋值构造函数, 与复制构造函数一样
// assignment constructor
template<typename T>
const RBT<T>& RBT<T>::operator=(const RBT &other) {
cnt = other.cnt;
if( cnt == 0 )
return *this;
std::queue<std::pair<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> > q;
q.push(std::make_pair(root(other.root->val),other.root));
while( !q.empty() ) {
TreeNode *node1 = q.front().first;
TreeNode *node2 = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if( node2->left ) {
node1->left = new TreeNode(node2->left->val);
node1->left->parent = node1;
q.push(make_pair(node1->left, node2->left));
}
if( node2->right ) {
node1->right = new TreeNode(node2->right->val);
node1->right->parent = node1;
q.push(make_pair(node1->right, node2->right));
}
}
return *this;
}
RBT<T> destructor函数,当对象不需要时释放内存
// destructor
template<typename T>
RBT<T>::~RBT() {
if( cnt == 0 )
return ;
cnt = 0;
std::queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while( !q.empty() ) {
root = q.front();
q.pop();
if( root->left ) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if( root->right ) {
q.push(root->right);
}
delete root;
}
}
RBT<T>的size()和empty()函数
size()函数返回当前BST<T>中的元素个数
// return the size of RBT
template<typename T>
const std::size_t RBT<T>::size() const {
return cnt;
}
empty()函数, 当BST<T>没有数据时返回true
// check whether the RBT is nullptr
template<typename T>
const bool RBT<T>::empty() const {
return cnt == 0;
}
RBT<T>的begi()和end()函数,分别返回对应的iterator
begin()函数需要首先找到BST<T>类的最左节点,然后返回其iterator实例
// iterator begin() and end()
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::iterator RBT<T>::begin() const {
TreeNode* node = root;
while( node && node->left )
node = node->left;
return iterator(node);
}
end()直接返回null iterator即可
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::iterator RBT<T>::end() const {
return iterator();
}
- 实现
insert(T v)来插入一个新的数据
对于
insert(T v)来说,我们可以和BST<T>一样,使用二分法将数据作为leaf node插入RBT<T>。和BST<T>不同的是,插入元素默认是RED node之后还要满足RBT的规则要求
// insert an element into RBT
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::insert(T v) {
insert(v,root);
// increase cnt
++cnt;
}
// private : insert an element into RBT
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::insert(T v, TreeNode *&r, TreeNode * const &p) {
if( r == nullptr ) {
r = new TreeNode(v, nullptr, nullptr, p);
// here we need to remove the violation of RBT if exists
insert_case1(r);
} else if( v < r->val )
insert(v, r->left, r);
else
insert(v, r->right,r);
}
当插入的元素作为
root节点,我们只需要将节点改成BLACK
// this function handle case that the current node is the root
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::insert_case1(TreeNode *r) {
// in this case we just paint the node to black
if( r->parent == nullptr )
r->color = BLACK;
else
insert_case2(r);
}
当插入节点的父节点是
BLACK node,新插入节点没有违反RBT规则,不需要操作
// this handles when the node's parent is black
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::insert_case2(TreeNode *r) {
// in this case we just return
if( r->parent->color == BLACK )
return;
else
insert_case3(r);
}
如下图所示,当插入节点
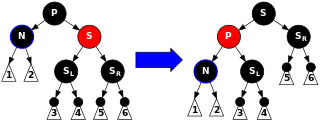
parent node和uncle node都是RED时,我们可以将parent node和uncle node改成BLACK,grandparent node改成RED,这样只有grandparent node违反RBT规则。所以需要从insert_case1()开始检查grandparent node。
// this handles when both the parent and the uncle are red
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::insert_case3(TreeNode *r) {
// when both the parent and the uncle are red, we can paint the parent and
// uncle to black and the grandParent to red
// this will remain all RBT rules but the grandParent may violate rule
TreeNode* u = uncle(r);
if( u && u->color == RED ) {
r->parent->color = BLACK;
u->color = BLACK;
u->parent->color = RED;
insert_case1(u->parent);
} else
insert_case4(r);
}
如下图所示,当插入节点
parent node是RED,而uncle node都是BLACK时,如果当前节点是左子树而其父节点是右子树,我们可以在父节点上进行rotate_right()操作。如果相反,则进行rotate_left()操作。
// this handles when current node's parent is red but the uncle is black
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::insert_case4(TreeNode *r) {
TreeNode *g = grandParent(r);
// when current node is the right child and parent is the left child of
// grandParent , we rotate left
if( r == r->parent->right && r->parent == g->left ) {
rotate_left(r->parent);
r = r->left;
// in this case we rotate right
} else if( r == r->parent->left && r->parent == g->right ) {
rotate_right(r->parent);
r = r->right;
}
insert_case5(r);
}
rotate_left(TreeNode *r)操作,就是将当前节点的右子树作为父节点而当前节点作为其左子树。
// this rotate the current node to the left
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::rotate_left(TreeNode *r) {
TreeNode *saved_right_left = r->right->left, *child = r->right;
if( r->parent ) {
if( r == r->parent->left )
r->parent->left = child;
else
r->parent->right = child;
// if current node is the root we need update the root node also
} else {
root = child;
}
child->left = r;
child->parent = r->parent;
r->parent = child;
r->right = saved_right_left;
if( saved_right_left )
saved_right_left->parent = r;
}
rotate_right(TreeNode *r)操作,就是将当前节点的左子树作为父节点而当前节点作为其右子树。
// thi rotate the current node to the right
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::rotate_right(TreeNode *r) {
TreeNode *saved_left_right = r->left->right, *child = r->left;
if( r->parent ) {
if( r == r->parent->left )
r->parent->left = child;
else
r->parent->right = child;
// if current node is the root we need update the root node also
} else {
root = child;
}
child->right = r;
child->parent = r->parent;
r->parent = child;
r->left = saved_left_right;
if( saved_left_right )
saved_left_right->parent = r;
}
如下图所示,当插入节点
parent node是RED,而uncle node都是BLACK时,我们可以将grandparent node变成RED,而父节点变成BLACK。如果当前节点和父节点都是左子树,对grandparent node进行rotate_right()操作,这样整个RBT<T>就满足所有平衡规则了。如果当前节点和父节点都是右子树则相反。
// this handles that the parent is red but uncle is black
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::insert_case5(TreeNode *r) {
TreeNode *g = grandParent(r);
// in this case we just paint the parent to BLACK and grandParent to RED
// then rotate left or right
g->color = RED;
r->parent->color = BLACK;
if( r == r->parent->left )
rotate_right(g);
else
rotate_left(g);
}
grandParent(TreeNode * const &r)函数得到当前节点的grandparent node
// get current node's grandparent
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::TreeNode* RBT<T>::grandParent(TreeNode * const &r) const {
if( r && r->parent )
return r->parent->parent;
else
return nullptr;
}
uncle(TreeNode * const &r)函数得到父节点的兄弟节点
// get current node's uncle
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::TreeNode* RBT<T>::uncle(TreeNode * const &r) const {
TreeNode *g = grandParent(r);
// if no grandParent then no uncle
if( g == nullptr )
return nullptr;
if( r->parent == g->left )
return g->right;
else
return g->left;
}
find(T v)查找数据是否存在, 与BST一致,只需要二分查找即可
// find an element
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::iterator RBT<T>::find(const T& v) const {
TreeNode *p = root;
while( p ) {
if( p->val == v )
return iterator(p);
if( p->val < v )
p = p->right;
else
p = p->left;
}
return end();
}
erase(iterator itr)删除数据
对于删除元素,和
insert(T v)类似, 可以先按照BST<T>的方法来处理,不过类似的,除此之外,当删除节点是BLACK时候还需要额外操作来保证满足RBT<T>的规则。当要删除的节点存在RED节点时我们只需要将其改成BLACK即可。
// remove one element
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::erase(iterator itr) {
--cnt;
if( cnt == 0 ) {
delete root;
root = nullptr;
return;
}
// if left & right child both exist
if( (itr.node)->left && (itr.node)->right ) {
TreeNode *predecessor = findMax((itr.node)->left);
(itr.node)->val = predecessor->val;
erase(iterator(predecessor));
} else {
TreeNode *child = (itr.node)->left ? (itr.node)->left : (itr.node)->right;
// here difference with bst, we need rebalance rbt to satisfy rbt rules
if( (itr.node)->color == BLACK ) {
// when current node is black and its child is RED, we can
// simply repaint child to black
if( child && child->color == RED )
child->color = BLACK;
// or the deleted node is the leaf cell, we should rebalance it
else
delete_case1(itr.node);
}
replace_node_in_parent(itr.node, child);
delete itr.node;
}
}
当要删除节点是
root node时不需要任何操作
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::delete_case1(TreeNode *node) {
// when current node is the new root , it's okay
if( node->parent != nullptr )
delete_case2(node);
}
如下图所示,当当前节点的兄弟节点是
RED时可以交换父节点与其兄弟节点的颜色。如果当前节点是左子树则对其父节点进行rotate_left()操作。反之则相反。
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::delete_case2(TreeNode *node) {
// in this case when current node's sibling is RED, we should replace its
// parent's color with its sibling, and rotate the parent
TreeNode *s = sibling(node);
if( s->color == RED ) {
node->parent->color = RED;
s->color = BLACK;
if( node == node->parent->left )
rotate_left(node->parent);
else
rotate_right(node->parent);
}
delete_case3(node);
}
对于下图所示
RBT<T>,如果当前节点兄弟节点,父节点以及兄弟节点的左右子节点都是BLACK,我们可以将其兄弟节点改成RED。
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::delete_case3(TreeNode *node) {
// in this case current node and its parent, its sibling and its sibling's
// two children are both black. we just repaint its sibling to red and
// rebalance the tree for its parent
TreeNode *s = sibling(node);
if( node->parent->color == BLACK && s->color == BLACK &&
(s->left == nullptr || s->left->color == BLACK) && (s->right == nullptr || s->right->color == BLACK) ) {
s->color = RED;
delete_case1(node->parent);
} else {
delete_case4(node);
}
}
下图所示是父节点是
RED而兄弟节点及其左右子节点都是BLACK,这种情况下我们只需要交换父节点和兄弟节点颜色即可。
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::delete_case4(TreeNode *node) {
// in this case current node and its sibling and its sibling's two children
// are all black but the parent is red, we can just exchange the parent and
// its sibling's color
TreeNode *s = sibling(node);
if( node->parent->color == RED && s->color == BLACK &&
(s->left == nullptr || s->left->color == BLACK) && (s->right == nullptr || s->right->color == BLACK) ) {
s->color = RED;
node->parent->color = BLACK;
} else {
delete_case5(node);
}
}
对于下图所示情况,即当前节点兄弟节点是
BLACK,如果有一个RED左子节点和BLACK右子节点可以交换兄弟节点及其左子节点的颜色,并对兄弟节点进行rotate_right()。反之则相反。
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::delete_case5(TreeNode *node) {
// in this case current node's sibling has a left red child and right black
// child, we can perform a right rotation on the sibling and exchange the
// color with its red child
TreeNode *s = sibling(node);
if( s->color == BLACK ) {
if( node == node->parent->left && (s->left && s->left->color == RED) &&
(s->right == nullptr || s->right->color == BLACK) ) {
s->color = RED;
s->left->color = BLACK;
rotate_right(s);
} else if( node == node->parent->right && (s->right && s->right->color == RED) &&
(s->left == nullptr || s->left->color == BLACK) ) {
s->color = RED;
s->right->color = BLACK;
rotate_left(s);
}
}
delete_case6(node);
}
对于下图所示情况,我们交换兄弟节点与父节点颜色,如果当前节点是左子节点,将兄弟节点右子节点改成
BLACK,然后对父节点rotate_left()
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::delete_case6(TreeNode *node) {
// in this case current node's sibling has a right red child
// we can perform rotate on current node's parent and exchange the color
// with sibling, and repaint the sibling's right red child to black
TreeNode *s = sibling(node);
s->color = node->parent->color;
node->parent->color = BLACK;
if( node == node->parent->left ) {
s->right->color = BLACK;
rotate_left(node->parent);
} else {
s->left->color = BLACK;
rotate_right(node->parent);
}
}
与
BST<T>一样,用子节点替换父节点
template<typename T>
void RBT<T>::replace_node_in_parent(TreeNode *node, TreeNode *newNode) {
if( node->parent ) {
if( node->parent->left == node )
node->parent->left = newNode;
else
node->parent->right = newNode;
} else {
root = newNode;
}
if( newNode )
newNode->parent = node->parent;
}
findMax(TreeNode *node)返回当前节点开始最大值
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::TreeNode *RBT<T>::findMax(TreeNode *node) {
while( node && node->right )
node = node->right;
return node;
}
sibling(TreeNode * const &r)函数得到当前节点的兄弟节点
// get current node's silbing
template<typename T>
typename RBT<T>::TreeNode* RBT<T>::sibling(TreeNode * const &r) const {
if( r == nullptr || r->parent == nullptr )
return nullptr;
if( r->parent->left == r )
return r->parent->right;
else
return r->parent->left;
}
测试程序
template<typename T>
void testTree() {
cout << endl;
int n = rand()%5;
int i = 0;
while( i++ < n ) {
T bst;
cout << "###########" << endl;
cout << "Test step : " << i << endl;
int m = rand()%10;
cout << "insert : ";
int v;
while( m-- ) {
v = rand()%100;
cout << v << "\t";
bst.insert(v);
}
cout << endl << "bst = ";
typename T::iterator itr = bst.begin();
while( itr != bst.end() ) {
cout << *itr << "\t";
itr++;
}
itr = bst.begin();
if( itr != bst.end() ) {
cout << endl << "after erase " << *itr << endl << "bst =";
bst.erase(itr);
}
itr = bst.begin();
while( itr != bst.end() ) {
cout << *itr << "\t";
itr++;
}
int x = v;
itr = bst.find(x);
if( itr != bst.end() ) {
cout << "\nFound " << x << ", now delete it" << endl;
bst.erase(itr);
} else {
cout << "\nCouldn't find " << x << endl;
}
cout << "bst = ";
itr = bst.begin();
while( itr != bst.end() ) {
cout << *itr << "\t";
itr++;
}
cout << "\nbst.size() = " << bst.size();
cout << endl << "###########" << endl;
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
cout << "Test BST<int>\n";
testTree<BST<int> >();
cout << "Test RBT<int>\n";
testTree<RBT<int> >();
return 0;
}
测试程序输出:
Test BST<int>
###########
Test step : 1
insert : 78 17
bst = 17 78
after erase 17
bst =78
Couldn't find 17
bst = 78
bst.size() = 1
###########
###########
Test step : 2
insert :
bst =
Couldn't find 17
bst =
bst.size() = 0
###########
Test RBT<int>
###########
Test step : 1
insert : 13 40 78 34 14 96 32 24 82
bst = 13 14 24 32 34 40 78 82 96
after erase 13
bst =14 24 32 34 40 78 82 96
Found 82, now delete it
bst = 14 24 32 34 40 78 96
bst.size() = 7
###########
###########
Test step : 2
insert : 4 82 42 87 81 28 74 54 95
bst = 4 28 42 54 74 81 82 87 95
after erase 4
bst =28 42 54 74 81 82 87 95
Found 95, now delete it
bst = 28 42 54 74 81 82 87
bst.size() = 7
###########
###########
Test step : 3
insert : 60 14 69
bst = 14 60 69
after erase 14
bst =60 69
Found 69, now delete it
bst = 60
bst.size() = 1
###########
###########
Test step : 4
insert : 62 23 15 31 34 31 22
bst = 15 22 23 31 31 34 62
after erase 15
bst =22 23 31 31 34 62
Found 22, now delete it
bst = 23 31 31 34 62
bst.size() = 5
###########
参考
1.wikipedia - binary search tree
2.wikipedia - red black tree