什么是B+ Tree?
说道B+ Tree不能不提B Tree, 所以下面先介绍B Tree结构和性质,再重点描述B+ Tree。
B Tree 的结构和性质
B Tree和BST类似,也是一种有序的搜索树,不同点是B Tree是M-ary的:
- 每一个内部节点最多有M-1个key, [M/2]到M个Children
- 叶子节点能够存储[(M-1)/2]到M-1个Key,并且所有叶子节点都是同样的深度
- 根节点可以有2到M个Children或者没有Children作为叶子节点
- 每个节点内Key从左到右递增,且大于左子树所有节点的Key,小于右子树所有节点的Key
可以发现当M = 2时B Tree就退化成一个平衡的BST了。当M=3时内部节点只能有2或者3个Children,也被称为2-3-tree。下图是一个典型的M=5的B Tree结构图:
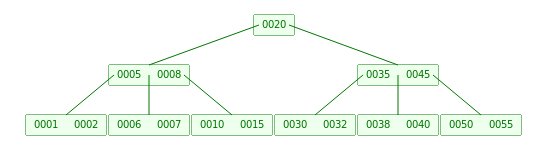
虽然相对于BST来说,每次IO读写能够操作的数据更多了,但是由于内部节点也存储了数据导致数据很大时不能将整个B Tree放进主存或缓存里,对IO操作仍然不友好。 所以就出现了下面的B+ Tree。
B+ Tree 的结构和性质
B+ Tree除了内部节点不存储数据外,和B Tree很类似:
- 每一个内部节点最多有M-1个key, [M/2]到M个Children,而且不存储对应的数据
- 叶子节点能够存储[L/2]到L个Key,同时还有对应的数据,并且所有叶子节点都是同样的深度
- 根节点可以有2到M个Children或者没有Children作为叶子节点
- 每个节点内Key从左到右递增,且大于左子树所有节点的Key,小于或等于右子树所有节点
相比于B Tree,可以发现如果L » M,大部份Key都在叶子节点,B+ Tree可以将整个B+ Tree放进主存或缓存里。下图是一个典型的当M = 5 L = 4的B+ Tree结构图:
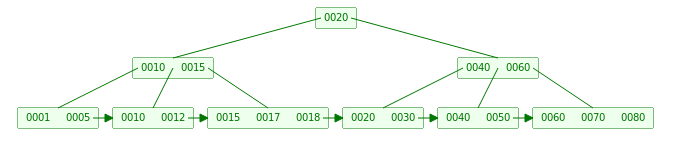
B+ Tree 实现
B+ Tree 类声明
类似 BST , B+ Tree 主要实现以下接口:
std::pair<bool, std::pair<_key, _data> > find(const _key& key) const: 查找key是否存在void insert(const _key &key, const _data &data): 插入<key,data>void erase(const _key& val): 删除valconst bool empty() const: 判断是否为空
完整代码可参考github - B+Tree
// BPlus Tree declaration
// the size of disk block
// default is 1024kb on linux
static const int BLOCK_SIZE = 1024;
// @param :
// _M : denote the maximum number key of innernode
// _L : denote the maximum number key of leafnode
template<typename _key,
typename _data,
// let innernode and leafnode contains allocated in a block default
int _M = ( BLOCK_SIZE - sizeof(void*) ) / ( sizeof(_key) + sizeof(void*) ),
int _L = BLOCK_SIZE / ( sizeof(_key) + sizeof(_data) )>
class BPlusTree {
public:
// default constructor
explicit BPlusTree();
// no assignment constructor & copy constructor
BPlusTree(const BPlusTree &other) = delete;
BPlusTree(BPlusTree &&) = delete;
const BPlusTree<_key,_data,_M,_L>& operator=(const BPlusTree &other) = delete;
// destructor
~BPlusTree();
// insert an element into BPlusTree
// current we don't support identical key
void insert(const _key &key, const _data &data);
// find an element, if true return key/data pair
// else return false pair
std::pair<bool, std::pair<_key, _data> > find(const _key& key) const;
// remove one element
void erase(const _key& val);
// return the size of BPlusTree
const std::size_t size() const;
// check whether the BPlusTree is nullptr
const bool empty() const;
// debug usage
// output leaf items
std::vector<std::pair<_key, _data> > dumpTree() const {
std::vector<std::pair<_key, _data> > res;
leafNode* n = head_;
while( n ) {
for(int i = 0; i < n->size_; ++i) {
res.push_back(std::make_pair(n->key_[i], n->data_[i]));
}
n = n->next_;
}
return res;
}
private:
class node;
class innerNode;
class leafNode;
/*
* template find function to search the key which is not less
* than specified key
*/
template<typename nodeType>
inline int find(nodeType *n, const _key& key) const {
unsigned int i;
for(i = 0; i < n->size_ && n->key_[i] < key; ++i);
return i;
}
/*
* const variables to hold the size limit of node
*/
// the number of inner node which may be different with the
// number of leaf node
static const int INNER_MAX_ = _M;
// the minimum number of inner node
static const int INNER_MIN_ = INNER_MAX_ / 2;
// the number of leaf node
static const int LEAF_MAX_ = _L;
// the minimum number of leaf node
static const int LEAF_MIN_ = LEAF_MAX_ / 2;
inline leafNode* newLeaf() {
leafNode* n = new leafNode();
++stats_.leaves_;
return n;
}
inline innerNode* newInner(unsigned int l) {
innerNode* n = new innerNode(l);
++stats_.inners_;
return n;
}
struct tree_stats {
std::size_t itemCount_; // number of items in btree
std::size_t leaves_; // number of leaf nodes
std::size_t inners_; // number of inner nodes
// default constructor
tree_stats() : itemCount_(0), leaves_(0), inners_(0) {};
};
// result flags of deletion
enum result_flag {
// deletion successful and no fix-ups necessary
btree_ok = 0,
// deletion not successful because key was not found
btree_not_found = 1,
// deletion successful, the last key was updated so parent need updates
btree_update_lastkey = 2,
// deletion successful, children nodes were merged and the parent
// needs to remove the empty node
btree_fixmerge = 4
};
// record the delet result status
struct result_t {
// result flag
result_flag flags_;
// the key to be updated at the parent's key
_key lastKey_;
// constructor of a result with specific flag, this can also
// be used as for implicit conversion
inline result_t(result_flag f = btree_ok) : flags_(f), lastKey_() {}
inline result_t(result_flag f, const _key& k) : flags_(f), lastKey_(k) {}
// test if result has a given flag set
inline bool has(result_flag f) const {
return (flags_ &f) != 0;
}
// operator overload
inline result_t& operator|=(const result_t& other) {
flags_ = result_flag(flags_ | other.flags_);
if( other.has(btree_update_lastkey) )
lastKey_ = other.lastKey_;
return *this;
}
};
// the root of b+tree
node *root_;
// the head which points to the first leaf node
leafNode* head_;
// the head which points to the last leaf node
leafNode* tail_;
// record the statistical information of tree
tree_stats stats_;
// private insert helper function
// TreeNode definition
// base class of node
class node {
public:
// no argument constructor
node() : level_(0), size_(0) {};
// constructor with one argument
node(unsigned int l) : level_(l), size_(0) {};
// record the current node's level, if 0, it's leaf node
unsigned int level_;
// record current node's size
unsigned int size_;
// method to check whether it's leaf or inner node
inline bool isLeafNode() const {
return level_ == 0;
}
};
// innernode can only store the key and pointer to child node
class innerNode : public node {
public:
// no argument constructor
innerNode() {};
// one argument constructor
innerNode(unsigned int l) : node(l) {}
// innernode only store keys and pointers to children
_key key_[INNER_MAX_];
node* child_[INNER_MAX_+1]; // child is one more than the key
inline bool isFull() const {
return node::size_ == INNER_MAX_;
}
inline bool isUnderflow() const {
return node::size_ < INNER_MIN_;
}
inline bool isFew() const {
return node::size_ >= INNER_MIN_;
}
};
// leaf node can store key/data pair
class leafNode : public node {
public:
// no argument constructor
leafNode() : prev_(nullptr), next_(nullptr) {};
// pointer to previous leafnode
leafNode* prev_;
// pointer to next leafnode
leafNode* next_;
// leafnode must store keys and data
_key key_[LEAF_MAX_];
_data data_[LEAF_MAX_];
inline bool isFull() const {
return node::size_ == LEAF_MAX_;
}
inline bool isUnderflow() const {
return node::size_ < LEAF_MIN_;
}
inline bool isFew() const {
return node::size_ >= LEAF_MIN_;
}
inline void setData(unsigned int idx, std::pair<_key, _data> val) {
assert( idx < LEAF_MAX_ );
key_[idx] = val.first;
key_[idx] = val.second;
}
};
void split_innernode(innerNode* n, node* &splitNode, _key& splitKey, unsigned int idx);
void split_leafnode(leafNode* n, node* &splitNode, _key& splitKey);
bool insert(node* node_, const _key& key, const _data& data, node* &splitNode, _key& splitKey);
result_t erase(const _key& val,node* n,node* left,node* right,innerNode* leftParent,innerNode* rightParent,innerNode* parent,unsigned int idxParent);
result_t shift_left_leaf(leafNode *left, leafNode *right, innerNode *parent, unsigned int idxParent);
void shift_left_inner(innerNode *left, innerNode *right, innerNode *parent, unsigned int idxParent);
void shift_right_leaf(leafNode *left, leafNode *right, innerNode *parent, unsigned int idxParent);
void shift_right_inner(innerNode *left, innerNode *right, innerNode *parent, unsigned int idxParent);
result_t merge_inner(innerNode* left, innerNode* right, innerNode* parent, unsigned int idxParent);
result_t merge_leaves(leafNode* left, leafNode* right, innerNode* parent);
};
B+ Tree 查找算法实现
类似于 BST 查找, 我们先在 inner node里找到第一个不小于
key值的数据,然后继续查找对应的字节点,只到到达叶子节点,然后在叶子节点查找key是否存在即可
// find an element, if true return key/data pair
// else return false pair
template<typename _key, typename _data, int _M, int _L>
std::pair<bool, std::pair<_key, _data> >
BPlusTree<_key,_data,_M,_L>::find(const _key& key) const {
node* n = root_;
if( !n )
return std::make_pair(false, std::make_pair(_key(), _data()) );
while( !n->isLeafNode() ) {
innerNode* tmp = static_cast<innerNode*>(n);
int idx = find(tmp, key);
n = tmp->child_[idx];
}
leafNode* leaf = static_cast<leafNode*>(n);
const unsigned int idx = find(leaf, key);
if( idx < leaf->size_ && leaf->key_[idx] == key )
return std::make_pair(true, std::make_pair(leaf->key_[idx], leaf->data_[idx]) );
return std::make_pair(false, std::make_pair(_key(), _data()) );
}
B+ Tree 插入算法实现
以上面的M = 5 L = 4的B+ Tree为例:
-
当插入16时,查找到 LeafNode 有3个key, 插入之后是4个key,满足LeafNode要求,所以直接插入就可
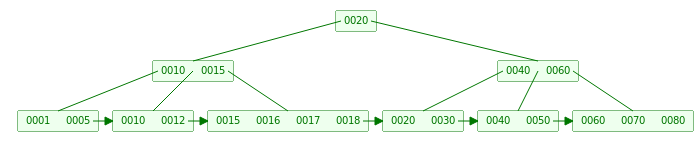
-
当我们继续插入19之后,LeafNode 的Key = 5 > L = 4,所以我们插入之后需要将这个 LeafNode 进行Split
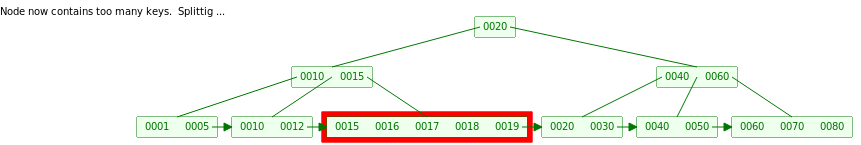
Split方法是将LeafNode从[L/2]处分成左右两个 LeafNode , 并将[L/2]处Key传递到父节点,父节点重复上面的插入动作
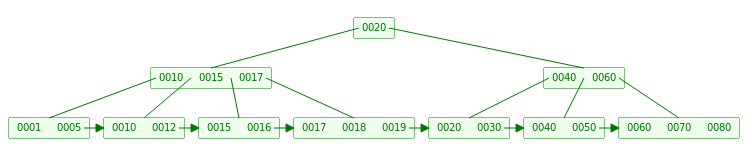
- 当我们向下面B+ Tree插入9时,LeafNode 需要Split
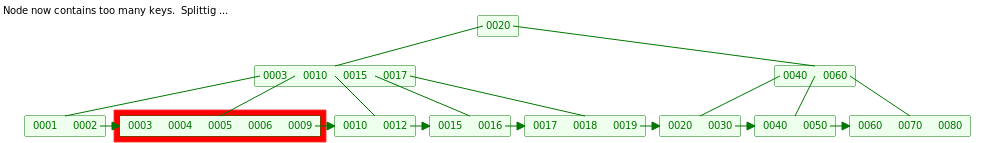
同时父节点插入传递上来的5之后也需要Split,同时传递10到根节点
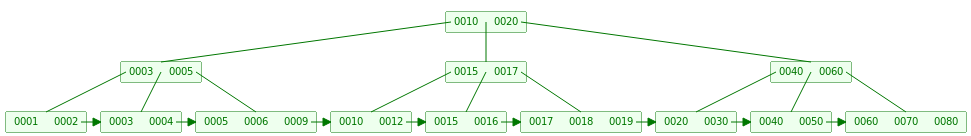
// insert an element into BPlusTree
// current we don't support identical key
template<typename _key, typename _data, int _M, int _L>
void BPlusTree<_key,_data,_M,_L>::insert(const _key& key, const _data& data) {
// if root_ is nullptr, first create the root node
if( root_ == nullptr )
root_ = head_ = tail_ = newLeaf();
// now we can descent down from the root
// if inner node has been split, we must handle if split propagates to root
node* newChild = nullptr;
_key newKey;
bool res = insert(root_, key, data, newChild, newKey);
// if newChild is not null, we must put the shiftup key into root
if( newChild ) {
innerNode* newRoot = newInner(root_->level_ + 1);
newRoot->key_[0] = newKey;
newRoot->child_[0] = root_;
newRoot->child_[1] = newChild;
newRoot->size_ = 1;
root_ = newRoot;
}
// after insertion, update the item count
if( res )
++stats_.itemCount_;
}
// insert helper function
// descent down to leaf and insert key/pair
// if the node overflows, then split the node and shiftup until root
template<typename _key, typename _data, int _M, int _L>
bool BPlusTree<_key,_data,_M,_L>::insert(node* node_, const _key& key,
const _data& data, node* &splitNode, _key& splitKey) {
if( node_->isLeafNode() ) {
leafNode* n = static_cast<leafNode*>(node_);
int idx = find(n, key);
// if key has already existed, just return
if( idx < n->size_ && n->key_[idx] == key )
return false;
if( n->isFull() ) {
split_leafnode(n, splitNode, splitKey);
// if the inserting key shold be in the new leaf node
if( idx >= n->size_ ) {
idx -= n->size_;
n = static_cast<leafNode*>(splitNode);
}
}
// insert key/data into node
std::copy_backward(n->key_ + idx, n->key_ + n->size_,
n->key_ + n->size_ + 1);
std::copy_backward(n->data_ + idx, n->data_ + n->size_,
n->data_ + n->size_ + 1);
n->key_[idx] = key;
n->data_[idx] = data;
++n->size_;
// if the inserted key/data is the first of leafnode
// we should update splitKey
if( splitNode && n == splitNode && idx == 0 )
splitKey = key;
return true;
} else {
innerNode* n = static_cast<innerNode*>(node_);
int idx = find(n, key);
// then descent down to child node
node* newChild = nullptr;
_key newKey;
bool res = insert(n->child_[idx], key, data, newChild, newKey);
// if newChild is not null, we must put the shiftup key into root
if( newChild ) {
if( n->isFull() ) {
split_innernode(n, splitNode, splitKey, idx);
// if the insrt key is in the splitNode
if( idx >= n->size_ + 1 ) {
idx -= n->size_ + 1;
n = static_cast<innerNode*>(splitNode);
} else if( idx == n->size_ + 1 && n->size_ < splitNode->size_ ) {
innerNode* tmp = static_cast<innerNode*>(splitNode);
// move the split key/child into the left node
n->key_[n->size_] = splitKey;
n->child_[n->size_+1] = tmp->child_[0];
++n->size_;
tmp->child_[0] = newChild;
splitKey = newKey;
return res;
}
}
std::copy_backward(n->key_ + idx, n->key_ + n->size_,
n->key_ + n->size_ + 1);
std::copy_backward(n->child_ + idx, n->child_ + n->size_ + 1,
n->child_ + n->size_ + 2);
n->key_[idx] = newKey;
n->child_[idx+1] = newChild;
++n->size_;
}
return res;
}
}
B+ Tree 删除算法实现
同样以上面插入之后的 M = 5 L = 4 的 B+ Tree 为例:
-
当删除18时,18所在 LeafNode 有3个Key,删掉之后Key = 2 >= L/2 = 2,所以直接删掉18即可
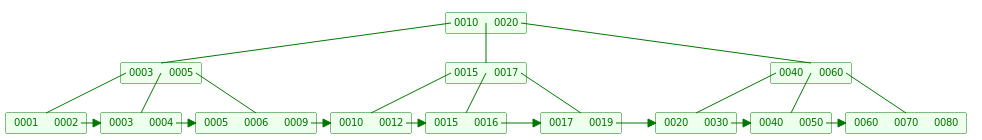
-
当继续删除16时,LeafNode 只有1个Key了,这时我们首先需要尝试从 Neighbor 吸收元素。但是左右Neighbor都只有L/2 = 2个Key,我们只能将当前 LeafNode 与 Neighbor 合并并更新父节点
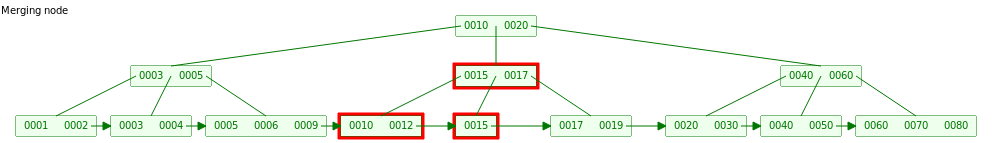
更新父节点之后发现父节点Key = 1 < [L/2],需要重复上面的删除动作(这儿也只能和Neighbor合并)
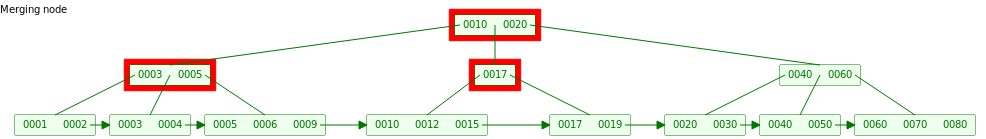
合并之后需要将父节点的10传递下来,最终树结构如下图:
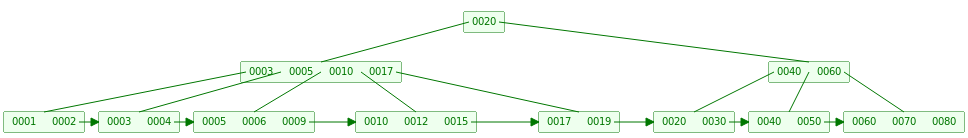
- 当继续删除17时,需要从Neighbor吸收元素15,同时更新父节点
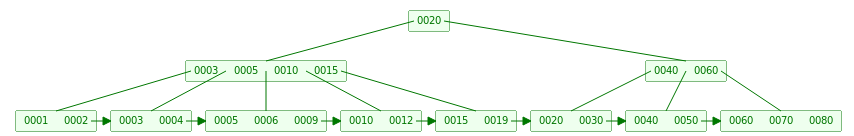
主要代码如下所示:
// remove one element
template<typename _key, typename _data, int _M, int _L>
void BPlusTree<_key,_data,_M,_L>::erase(const _key& val) {
if( !root_ )
return;
result_t res = erase(val, root_, nullptr, nullptr,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr, 0);
if( !res.has(btree_not_found) )
--stats_.itemCount_;
}
// descends down the tree for searching the key
// and remove it after found
template<typename _key, typename _data, int _M, int _L>
typename BPlusTree<_key,_data,_M,_L>::result_t BPlusTree<_key,_data,_M,_L>::erase(const _key& val,
node* n,
node* left,
node* right,
innerNode* leftParent,
innerNode* rightParent,
innerNode* parent,
unsigned int idxParent
) {
if( n->isLeafNode() ) {
leafNode* leaf = static_cast<leafNode*>(n);
leafNode* leftLeaf = static_cast<leafNode*>(left);
leafNode* rightLeaf = static_cast<leafNode*>(right);
int idx = find(leaf, val);
if( idx >= leaf->size_ || leaf->key_[idx] != val )
return btree_not_found;
// if found , then erase the key
std::copy(leaf->key_ + idx + 1, leaf->key_ + leaf->size_, leaf->key_ + idx);
std::copy(leaf->data_ + idx + 1, leaf->data_ + leaf->size_, leaf->data_ + idx);
--leaf->size_;
result_t res = btree_ok;
// if the key is the last one
if( idx == leaf->size_ ) {
if( parent && idxParent < parent->size_ )
parent->key_[idxParent] = leaf->key_[leaf->size_ - 1];
else {
if( leaf->size_ >= 1 ) {
res |= result_t(btree_update_lastkey, leaf->key_[leaf->size_-1]);
}
}
}
if( leaf->isUnderflow() && !( leaf == root_ && leaf->size_ >= 1 ) ) {
// case1 : if leaf == root, then reset to null
if( leftLeaf == nullptr && rightLeaf == nullptr ) {
root_ = nullptr;
leaf = nullptr;
head_ = tail_ = nullptr;
return btree_ok;
}
// case2 : if both left and right leaves would underflow because of
// shift, then merge them
else if( (leftLeaf == nullptr || leftLeaf->isFew()) && (rightLeaf == nullptr || rightLeaf->isFew()) ) {
if( leftParent == parent )
res |= merge_leaves(leftLeaf, leaf, parent);
else
res |= merge_leaves(leaf, rightLeaf, parent);
}
// case3: the right leaf has extra data, balance it
else if( (leftLeaf && leftLeaf->isFew()) && (rightLeaf && !rightLeaf->isFew()) ) {
if( rightParent == parent )
res |= shift_left_leaf(leaf, rightLeaf, rightParent, idxParent);
else
res |= merge_leaves(leftLeaf, leaf, leftParent);
}
// case4 : the left leaf has extra data, so balance left
else if( (leftLeaf && !leftLeaf->isFew()) && (rightLeaf && rightLeaf->isFew()) ) {
if( leftParent == parent )
shift_right_leaf(leftLeaf, leaf, leftParent, idxParent-1);
else
res |= merge_leaves(leaf, rightLeaf, rightParent);
}
// case5 : both leaves have extra data, choose more data leaf
else if( leftParent == rightParent ) {
if( leftLeaf->size_ <= rightLeaf->size_ )
res |= shift_left_leaf(leaf, rightLeaf, rightParent, idxParent);
else
shift_right_leaf(leftLeaf, leaf, leftParent, idxParent-1);
} else {
if( leftParent == parent )
shift_right_leaf(leftLeaf, leaf, leftParent, idxParent-1);
else
res |= shift_left_leaf(leaf, rightLeaf, rightParent, idxParent);
}
}
return res;
} else {
innerNode* inner = static_cast<innerNode*>(n);
innerNode* leftInner = static_cast<innerNode*>(left);
innerNode* rightInner = static_cast<innerNode*>(right);
node* myleft, *myright;
innerNode* myleftParent, *myrightParent;
int idx = find(inner, val);
if( idx == 0 ) {
myleft = left ? (static_cast<innerNode*>(left))->child_[left->size_-1] : nullptr;
myleftParent = leftParent;
} else {
myleft = inner->child_[idx-1];
myleftParent = inner;
}
if( idx == inner->size_ ) {
myright = right ? (static_cast<innerNode*>(right))->child_[0] : nullptr;
myrightParent = rightParent;
} else {
myright = inner->child_[idx+1];
myrightParent = inner;
}
result_t res = erase(val, inner->child_[idx], myleft, myright,
myleftParent, myrightParent, inner, idx);
result_t myRes = btree_ok;
if( res.has(btree_not_found) )
return res;
if( res.has(btree_update_lastkey) ) {
if( parent && idxParent < parent->size_ )
parent->key_[idxParent] = res.lastKey_;
else
myRes |= result_t(btree_update_lastkey, res.lastKey_);
}
if( res.has(btree_fixmerge) ) {
// either current node or the next is empty and should be removed
if( inner->child_[idx]->size_ != 0 )
++idx;
std::copy(inner->key_+idx, inner->key_+inner->size_, inner->key_+idx-1);
std::copy(inner->child_ +idx+1, inner->child_ +inner->size_+1, inner->child_+idx);
--inner->size_;
if( inner->level_ == 1 ) {
--idx;
leafNode* child = static_cast<leafNode*>(inner->child_[idx]);
inner->key_[idx] = child->key_[child->size_-1];
}
}
if( inner->isUnderflow() && !(inner == root_ && inner->size_ >= 1) ) {
// case1 : the inner node is the root and has just one child, the
// child becomes the new root
if( leftInner == nullptr && rightInner == nullptr ) {
root_ = inner->child_[0];
inner->size_ = 0;
return btree_ok;
}
// case2 : if both left and right leaves would underflow if shift,
// then merge them
else if( (!leftInner || leftInner->isFew()) && (!rightInner || rightInner->isFew()) ) {
if( leftParent == parent )
myRes |= merge_inner(leftInner, inner, leftParent, idxParent-1);
else
myRes |= merge_inner(inner, rightInner, rightParent, idxParent);
}
// case3 : the right leaf has extra data, so balance right with
// current
else if( (leftInner && leftInner->isFew()) && (rightInner && !rightInner->isFew()) ) {
if( rightParent == parent )
shift_left_inner(inner, rightInner, rightParent, idxParent);
else
myRes |= merge_inner(leftInner, inner, leftParent, idxParent-1);
}
// case4 : the left leaf has extra data, so balance left
else if( (leftInner && !leftInner->isFew()) && (rightInner && rightInner->isFew()) ) {
if( leftParent == parent )
shift_right_inner(leftInner, inner, leftParent, idxParent-1);
else
myRes |= merge_inner(inner, rightInner, rightParent, idxParent);
}
// case5 : both the leaf and right leaves have extra data
else if( leftParent == rightParent ) {
if( leftInner->size_ <= rightInner->size_ )
shift_left_inner(inner, rightInner, rightParent, idxParent);
else
shift_right_inner(leftInner, inner, leftParent, idxParent-1);
} else {
if( leftParent == parent )
shift_right_inner(leftInner, inner, leftParent, idxParent-1);
else
shift_left_inner(inner, rightInner, rightParent, idxParent);
}
}
return myRes;
}
}
测试程序
对B+Tree的接口简单测试一下 :
#include "btree.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include<cstddef>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
BPlusTree<int, int, 2, 2> b;
assert( b.empty() );
b.insert(10,20);
assert( b.size() == 1 );
auto r = b.find(20);
assert( r.first == false );
r = b.find(10);
assert( r.first == true );
assert( r.second == make_pair(10,20) );
b.insert(20,20);
r = b.find(20);
assert( r.first == true );
assert( r.second == make_pair(20,20) );
b.insert(20,20);
r = b.find(20);
assert( r.first == true );
assert( r.second == make_pair(20,20) );
b.insert(30,20);
r = b.find(30);
assert( r.first == true );
assert( r.second == make_pair(30,20) );
r = b.find(40);
assert( r.first == false );
b.insert(40,20);
r = b.find(40);
assert( r.first == true );
assert( r.second == make_pair(40,20) );
b.insert(50,20);
r = b.find(50);
assert( r.first == true );
assert( r.second == make_pair(50,20) );
vector<pair<int, int> > res = b.dumpTree();
assert( res.size() == 5 );
for(int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i)
assert( res[i] == make_pair(10 * ( i + 1 ), 20) );
b.erase(50);
assert(b.size() == 4);
r = b.find(50);
assert( r.first == false );
b.erase(40);
assert(b.size() == 3);
r = b.find(40);
assert( r.first == false );
res = b.dumpTree();
assert( res.size() == 3 );
for(int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i)
assert( res[i] == make_pair(10 * ( i + 1 ), 20) );
cout << "-- Test Pass --" << endl;
return 0;
}
